By Byte & Block — exploring the building blocks of digital finance.
So… What Actually Is a Blockchain 🌐⛓️?
You hear about it everywhere — in crypto headlines, government papers, even your cousin’s group chat.
But ask ten people what a blockchain actually is, and you’ll get ten different answers.
So let’s cut the noise.
Blockchain isn’t magic, and it’s not just about “coins.” 🌕🌕🌕🌕
It’s a new way to agree on what’s true — digitally — without trusting a middleman.
🧱 1. The Problem Blockchain Tried to Solve
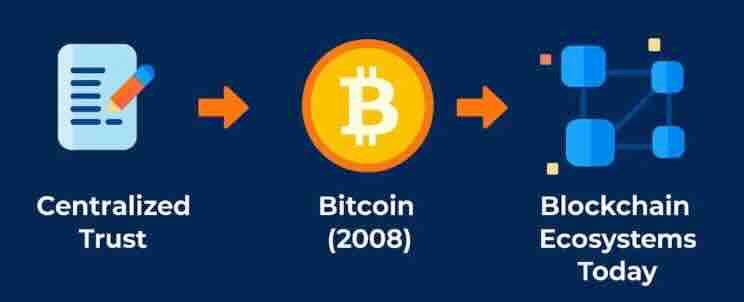
For most of human history, we’ve relied on institutions to verify truth — banks to confirm balances, governments to record ownership, and corporations to manage data.
That works… until it doesn’t.
Data can be changed, fees add friction, and trust can be lost.
In 2008, a pseudonymous developer named Satoshi Nakamoto proposed an alternative:
a network where people could transact without intermediaries, using cryptography instead of corporate or government trust.
That’s how the first blockchain — Bitcoin ₿₿ — was born 🚀.
🔗 2. The Core Idea: A Ledger That No One Owns


Think of blockchain like a shared Google Sheet that:
- Everyone can view,
- No one can edit without everyone else seeing, and
- Every new entry is locked to the one before it.
Each new “block” of transactions includes a digital fingerprint — a hash — of the previous one.
That creates an unbreakable chain of records, updated by thousands of independent computers (nodes) at once.
Instead of one central server, data lives everywhere at once.
That’s decentralization — and it’s what gives blockchain its resilience.
⚙️ 3. How the Network Stays Honest

Here’s where it gets clever.
How do you keep everyone honest if anyone can join the network?
Blockchains use a consensus mechanism — rules for agreeing on what’s true.
- Proof of Work (Bitcoin): 🤖 computers compete to solve puzzles → winner adds the next block.
- Proof of Stake (Ethereum, Solana): participants “lock up” coins to verify transactions → rewarded for good behavior 💸, penalized for cheating.
Both methods reward accuracy and punish fraud, making the system self-enforcing.
🌐⛓️ 4. Why It Matters Beyond Crypto

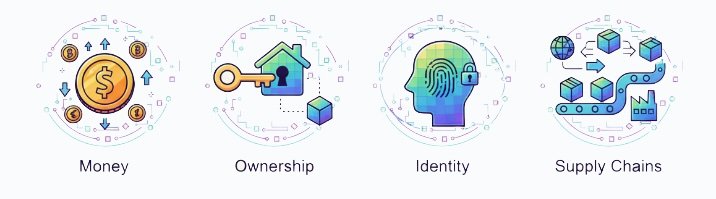
The same technology behind digital coins also enables:
- Digital ownership: NFTs prove who owns a piece of art or game item 👾.
- Transparent supply chains: track goods from source to store.
- Decentralized finance (DeFi): open financial tools without banks.
- Digital identity: cryptographic proof of “you” online.
Even major corporations are testing blockchain for record-keeping, auditing, and logistics.
And governments? They’re experimenting with central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) that use similar principles.
⚖️ 5. The Trade-Offs
Blockchain isn’t perfect.
It trades efficiency for transparency — storing every transaction publicly can make systems slower.
Some networks consume heavy energy (though newer designs are improving).
And regulation is still catching up.
The important part: these are growing pains of a young technology — not failures.
Each generation of networks gets more efficient, private, and accessible.
💡 6. The Takeaway: Trust Is Going Digital
Whether you ever buy crypto or not, blockchain represents a shift in how we define trust.
For the first time, we can create digital systems that verify themselves — no bank, company, or government required.
That’s the real story here — not tokens or speculation, but a new layer of internet infrastructure built on cryptography and consensus.
The last era of the web connected people.
The next connects trust.
💬 What’s Next

Over the next few weeks, we’ll explore:
- How stablecoins are reshaping digital money
- The link between AI and blockchain
- What decentralization really means for users
Follow @byte_and_block for bite-sized insights, or subscribe to the newsletter for deeper dives.
Subscribe to our newsletter!